[SQL]: Subscription Application
SQL
Node.js
10/02/2019
This post uses a light weight Nods.js framework, Express to create a web app that takes users' subscription and store into mysql database.
More Node frameworks can be found from Node frameworks
Express
Create package.json
$ npm initCreates package.json acts as a log file that records which package & versions were installed. For example, installation using npm install, will look up package.json and install all necessary packages at once.
$ npm initThis utility will walk you through creating a package.json file.It only covers the most common items, and tries to guess sensible defaults.
See `npm help json` for definitive documentation on these fieldsand exactly what they do.
Use `npm install <pkg>` afterwards to install a package andsave it as a dependency in the package.json file.
Press ^C at any time to quit.package name: (subscription)version: (1.0.0)description:entry point: (index.js) app.jstest command:git repository:keywords:author:license: (ISC)About to write to /workspace/mySQL4613/subscription/package.json:
{ "name": "subscription", "description": "",, "description": "",, "main": "app.js", "scripts": { "test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1" }, "author": "", "license": "ISC"}Is this OK? (yes)Install Express
$ npm i express--save flag saves express into json file, but current npm supports it as default
Install Faker, MySQL
$ npm i faker mysqlUpdated package.json
{ "name": "subscription", "version": "1.0.0", "description": "", "main": "app.js", "scripts": { "test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1" }, "author": "", "license": "ISC", "dependencies": { "express": "^4.17.1", "faker": "^4.1.0", "mysql": "^2.17.1" }}Installing them with package.json
When you have above json file, you can run
$ npm installTo install all the packages automatically
Request & Response (GET)
Create app.js file
var express = require("express") // import the packagevar app = express() // execute entire expressvar path = "/"
app.get(path, function(req, res) { res.send("hello worlddd")})Client --> Express App(Node)
On opening a web page, client sends a request to the Express app.
Express App --> Client
On request from the client, the web needs to respond
The following code adds a route where the app will respond after the user requests to the app with specified path
app.get(path, function(req, res) { console.log("request was sent") //console.log(req); res.send("hello worlddd") // app responding to client})- res: response object
- You can't have more than one res.send(), but normally we'll response with a file
- req: incoming request
- Later we'll reuse request to send email address
- Every route needs a call back function() which happens after a function
- console.log(req) will give you a detailed information about the request
Starts the server
var port = 3000app.listen(port, function() { console.log("Server running on port" + port)})You can also specify the port in shell with the following:
app.listen(process.env.PORT || 3000, process.env.IP, () => { console.log("Server running")})To run,
$ PORT=3000 node app.jsAdding more routes
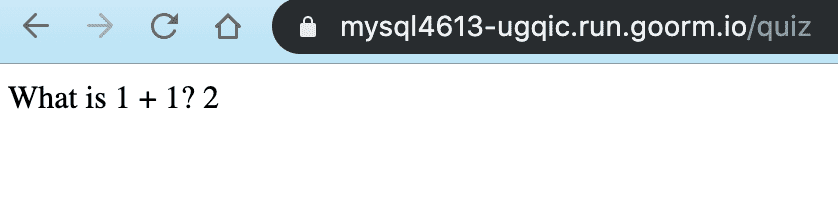
app.get("/quiz", function(req, res) { var question = "What is 1 + 1? 2" res.send(question)})
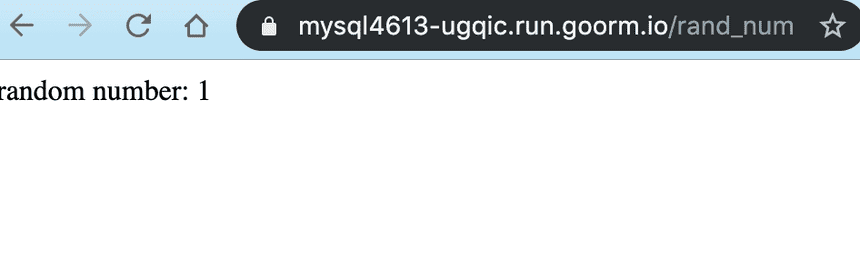
app.get("/rand_num", function(req, res) { console.log("request was sent on rand_num") // Random# between 1 ~ 10 var num = Math.floor(Math.random() * 10 + 1) res.send("random number: " + num)})Results:
Integration with MySQL
Client --> Express App --> MySQL
With MySQL Node.js Package, the request gets sent from client.
MySQL --> Express App --> Client
MySQL gives data back(responds) to the app and displays the information to the user.
Connect to MySQl
Create & Connect to the database. Reference from this post.
var mysql = require("mysql")var express = require("express")var app = express()
var connection = mysql.createConnection({ host: "localhost", user: "root", database: "subscription_db",})
var path = "/"app.get(path, function(req, res) { console.log("request was sent")
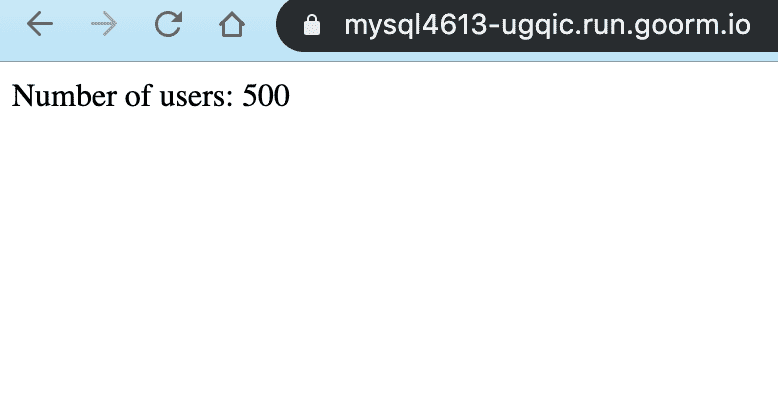
// Get # users from query var q = "SELECT COUNT(*) AS total FROM users" connection.query(q, function(error, results, fields) { if (error) throw error var num_users = results[0].total res.send("Number of users: " + num_users) })})
var port = 3000app.listen(port, function() { console.log("Server running on port" + port)})// connection.end();- Make sure that your mysql server is running beforehand
- It's better to send the response inside the callback of query
- In a running web server, we don't explicitly end the connection. It will end when the server is shut down or when we close the container
Output:
Add HTML with EJS
Bad example
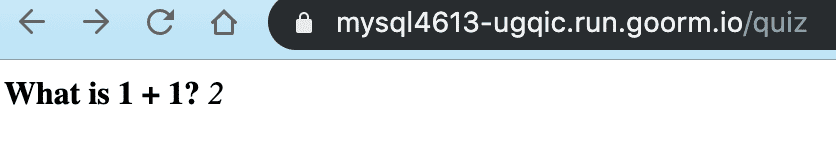
app.get("/quiz", function(req, res) { var question = "<strong>What is 1 + 1?</strong> <em>2</em>" res.send(question)})Output:
Install EJS package
npm i ejsEJS(embedded JavaScript) is a templating language that's an alternative to writing plain HTML.
It's an HTML that allows to embed JavaScript inside. Regular HTML itself can't contain a dynamic variables.
Change templating engine
app.set("view engine", "ejs")Change express' templating engine to ejs.
Create /views/home.ejs
<h1>Join our Mailing List!</h1><p> Would you like to receive mailings from special offers and events?<br /> We have <strong>123,456</strong> people joined our list!</p><form> <input type="text" class="form" placeholder="Your email" /> <button> Sign up </button></form>Loads file in request
var path = "/"app.get(path, function(req, res) { var q = "SELECT COUNT(*) AS total FROM users" connection.query(q, function(error, results, fields) { if (error) throw error var num_users = results[0].total res.render("home") })})res.render("home")Look for home.ejs file inside views directory (default). Extension is whatever we set previously.
Output:
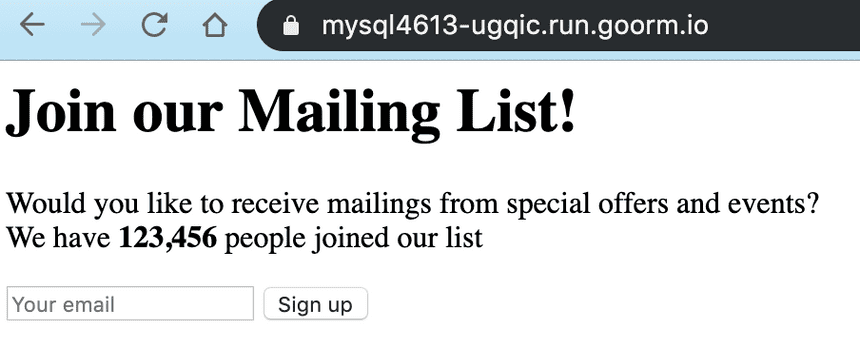
Pass in JS object
res.render("home", { num: num_users })Send home.ejs the data, numusers. It will be accessed with _num in home.ejs
Usage to send in multiple variables
res.render("fileName", { varInEjs: varInJS, varInEjs2: varInJS2 })Retrieve inside home.ejs
<p>... We have <strong><%=num%></strong> people joined our list!</p>Use the following to access data passed in
<%=num%>We can also insert JavaScript inside
<%= %>in ejs files.
GET & POST requests
GET
When you send a GET request
<form method="GET" action="/quiz"> <!-- ... --></formit will send data to quiz as GET on submit button. i.e. This will route to /quiz page because we already have app.get() route for quiz:
app.get("/quiz", function(req, res) { res.send("What is 1 + 1? 2")})? in URL
https://mysql4613-ugqic.run.goorm.io/quiz?You'll notice ? at the end of url after submit because no data is being sent. We haven't assigned a name to save it under.
Assign the name with the following
<input name="email" ... /><form method="GET" action="/quiz"> <input name="email" type="text" class="form" placeholder="Your email" /> <button> Sign up </button></form>Now when you send an email, for example, [email protected], it will append the string on the url.
https://mysql4613-ugqic.run.goorm.io/quiz?email=asd%40gmail.comThough this appended string may be useful for searching forms, the standard way of sending data from a form adding into database is to use POST request.
POST
<form method="POST" action="/register"> <!-- ... --></form>method="POST" action="/register"When the form is submitted with the button, it will be a POST request and send it to the router /register.
Define route for POST request
app.post("/register", function(req, res) { // POST route})If you try going to url /register, that will be a GET request i.e. only way to get to this route is to submit the form.
body-parser
body-parser parses the request body. i.e. it'll find email="[email protected]" from the sent POST request. It will return in JavaScript which we can manipulate.
Install body-parser
$ npm i body-parserConfigure
//...var bodyParser = require("body-parser")app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true }))app.js
var mysql = require("mysql")var express = require("express")var bodyParser = require("body-parser")
// Configure appvar app = express()app.set("view engine", "ejs")app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true }))// ...Extract form data from request body
app.post("/register", function(req, res) { console.log("post request sent to /register: \nReceived: " + req.body.email)})email came from ejs file where <input name="" ...>
Insert into database
app.post("/register", function(req, res) { var person = { email: req.body.email, } connection.query("INSERT INTO users SET ?", person, function(err, result) { if (err) throw err res.send("Thank you for joining!") // console.log(result); })})You can redirect to home page, app.get('/'..) with res.redirect('/');
Add CSS
Create public/app.css
body { font-family: "Be Vietnam", sans-serif; text-align: center; text-shadow: 0 0.05rem 0.1rem rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.4); color: Ivory; height: 100%; background-image: url("https://i.imgur.com/5cYE4ui.png"); background-size: cover; font-weight: 100; /*thinner text*/}
h1 { margin: 0; font-size: 50px; line-height: 300px; font-weight: 100;}
p { margin: 0; font-size: 30px;}
.form { margin-top: 50px; line-height: 1.5; border: none; border-bottom: 2px solid #ffffff; width: 500px; color: #94ecd2; font-family: "Turret Road", cursive; font-size: 3em; background: transparent; padding: 10px 10px;}
::placeholder { color: LightGray; font-size: 70%;}
input[type="text"]:focus { outline: none;}
button { border: none; border: 3px solid white; padding: 6px 20px; color: rgb(69, 69, 69); line-height: 2; font-size: 1.3em; background: rgba(255, 255, 255, 1); border-radius: 5px; opacity: 0.7;}
.flex-container { display: flex; justify-content: center; flex-direction: column; height: 100%;}Add connection in app.js
app.use(express.static(__dirname + "/public"))Take everything in /public directory and make them accessible by our views.
Add connection in home.ejs & Google fonts
<head> <link rel="stylesheet" href="/app.css" /> <link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Be+Vietnam&display=swap" rel="stylesheet" /> <link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Turret+Road&display=swap" rel="stylesheet" /></head><!-- ... -->Surround div in HTML
<body> <div class="flex-container"> <div class="container"> <h1>Join our Mailing List!</h1> <p> Would you like to receive mailings from special offers and events? <br /> We have <strong> <%=num%> </strong> people joined our list! </p> <form method="POST" action="/register"> <input name="email" type="text" class="form" placeholder="Your email" /> <button> Sign up </button> </form> </div> </div></body>app.js
var mysql = require("mysql")var express = require("express")var bodyParser = require("body-parser")
// Configure appvar app = express()app.set("view engine", "ejs")app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true }))app.use(express.static(__dirname + "/public"))
var connection = mysql.createConnection({ host: "localhost", user: "root", database: "subscription_db",})
var path = "/"app.get(path, function(req, res) { var q = "SELECT COUNT(*) AS total FROM users" connection.query(q, function(error, results, fields) { if (error) throw error var num_users = results[0].total res.render("home", { num: num_users }) })})
app.post("/register", function(req, res) { var person = { email: req.body.email, } connection.query("INSERT INTO users SET ?", person, function(err, result) { if (err) throw err res.redirect("/") })})
var port = 3000app.listen(port, function() { console.log("Server running on port" + port)})