[React + Node.js]: Deploy Your MERN Stack App to Amazon EC2 with SSL Encryption
deploy
03/18/2020
This post is stale
Stale because using Route 53 & Elastic Load Balancer & Amazon Certificate Manager are not necessary. i.e. this post tells to use both Certificate Manager and letsencrypt that are duplicate processes. New post is available here
Heroku vs Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Both are popular choices for cloud services where you can deploy your web applications and are great for hosting them. Heroku, in my opinion, is a lot simpler when it comes to deploy MERN stack application, but I still wanted to cover them both.
Prerequisites
If you don't have MERN Stack project available, here is how you can set up a basic MERN stack application with REST API.
- [React + Node.js]: Create your MERN Stack Application - Part 1: Backend
- [React + Node.js]: Create your MERN Stack Application - Part 2: Frontend
In addition, be sure to go through some steps from the last post on how to..
You can choose skip above steps and download the project. I'll be using this project to deploy on AWS EC2.
1. Create Ubuntu AWS EC2 Instance
Go to AWS console to sign up with your account if you haven't. Once singed in, Launch a virtual machine
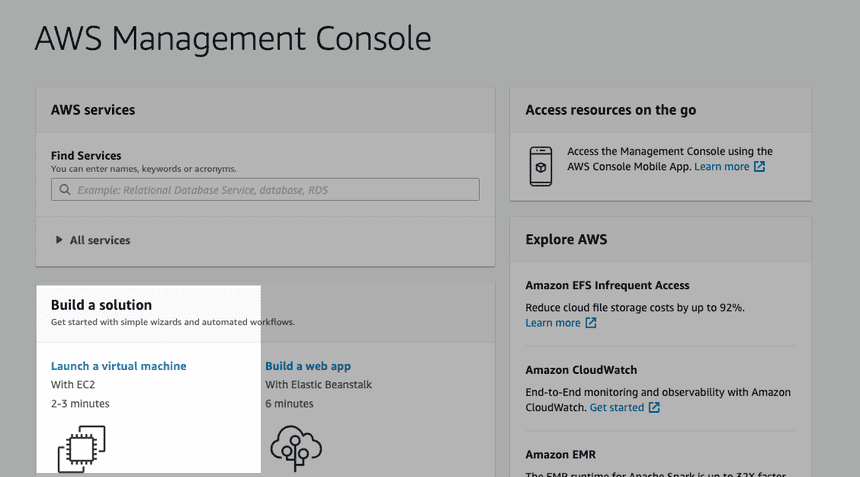
Search for ubuntu and select Ubuntu Server 18.04 LTS (HVM), SSD Volume Type
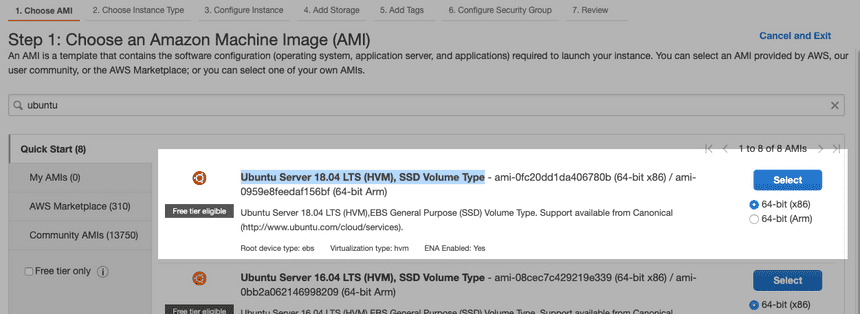
Make sure that t2.micro (Free tier eligible) is checked and click 6. Configure Security Group.
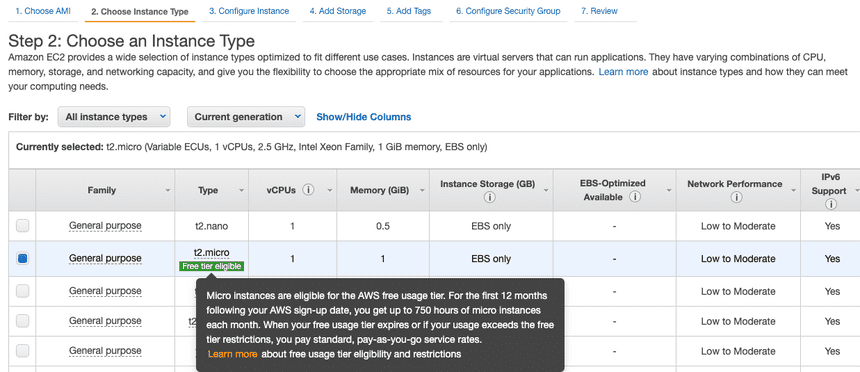
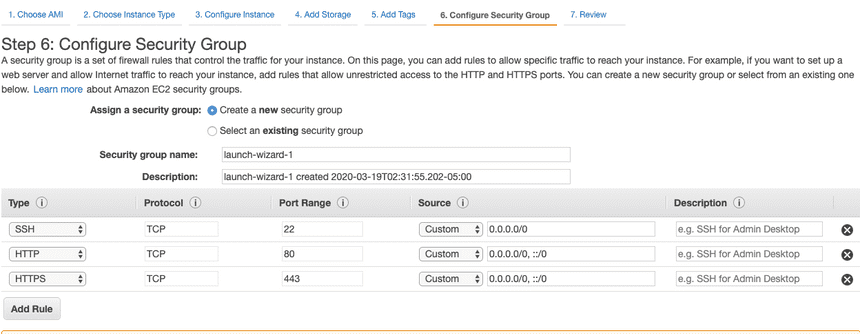
Add more types: HTTP and HTTPS by clicking Add Rule. Once added, click Review and Launch
Click Launch
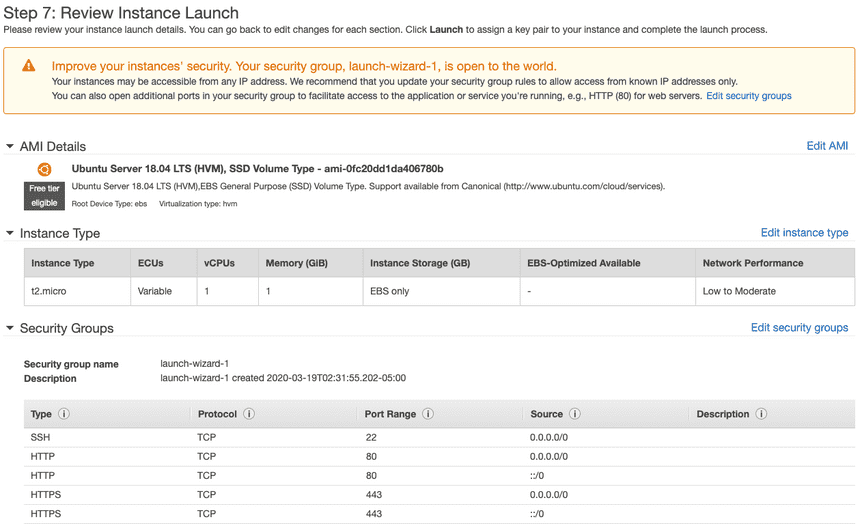
Create a new key pair. Name your key (filename), Download Key Pair then click Launch Instances
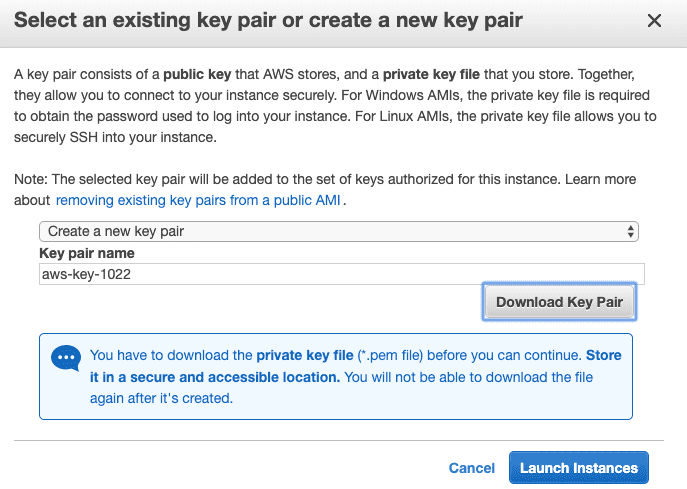
Click View Instances
Under Description tab, copy your Public DNS (IPv4) as you'll need it soon

2. Connect to your Instance
Open your git bash(windows) or terminal(mac) then browse over to the directory you saved your key file. Then run the command to change file access (User can read only).
chmod 400 ~/Downloads/aws-key-1022.pemThen connect to your instance with your copied Public DNS (IPv4). i.e. ssh -i ~/Downloads/aws-key-1022.pem [email protected]
ssh -i ~/Downloads/aws-key-1022.pem ubuntu@<YOUR_COPIED_PUBLIC_DNS>3. Install required packages on Ubuntu
Run the below command to install all packages needed to run the server on Ubuntu.
curl https://ellismin.com/sh/linux-mern-setup | sudo bashWhat's in file: linux-mern-setup
# Add nodejs 10 personal package from nodesourcecurl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_10.x | sudo -E bash -# Install Node.js & npmsudo apt-get install -y nodejs# Import GPK key for MongoDBsudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv 4B7C549A058F8B6B# Add MongoDB APT repository at /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb.listecho "deb [ arch=amd64 ] https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu bionic/mongodb-org/4.2 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb.list# Instal MongoDB on Ubuntusudo apt updatesudo apt-get install -y mongodb-org# Start MongoDBsudo systemctl start mongod# Start MongoDB automatically on startupsudo systemctl enable mongod# Install pm2sudo npm install -g pm2# Start pm2 automatically on startupsudo pm2 startup systemd# Install nginxsudo apt-get install -y nginx# Enable UWF--allow SSH with firewallsudo ufw allow OpenSSH# Allow HTTP/HTTPS with firewallsudo ufw allow 'Nginx Full'# Enable firewallsudo ufw --force enable4. Set up your MERN application with nginx
Clone your repository into your Ubuntu machine. Note that I'm using a project that was set up in this post. Client folder(front-end) is located inside the root directory that contains other the back-end code.
sudo git clone https://github.com/EllisMin/mern-demo-production.git /opt/mern-demoTired of github authentication for pulling repository? Create ssh-keygen with
cd ~/.ssh & ssh-keygenthen keep pressing enter for prompts. Runcat id_rsa.pubto copy the key & paste into github repository -->Settings-->Deploy keys-->Add deploy key.
Navigate into project folder and install npm packages
cd mern-demo && sudo npm iStart the server with pm2
sudo pm2 start app.jsWhy use pm2? While running the server with
npm startworks, the server may crash if there's an error or unexpected behavior occur to the server. pm2 allows to keep application alive forever by reloading Node.js application without downtime.
Tip: more commands for pm2
# You can use [filename] instead of allsudo pm2 stop all # Stops all process running with pm2sudo pm2 restart all # Restart all process runningsudo pm2 delete all # Remove all process from pm2 listsudo pm2 logs # Displays log messagessudo pm2 status # Shows status of running serversConfiguring nginx
Start off by removing the default setting for nginx
sudo rm /etc/nginx/sites-available/defaultThen, create a new default for configuration
sudo vim /etc/nginx/sites-available/default# ORsudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/default/etc/nginx/sites-available/default
server { listen 80 default_server; server_name _; # Path to front-end index.html location / { root /opt/mern-demo/front-end/build; try_files $uri /index.html; }}Change the path to your project's build folder of client side.
i.e.
/opt/<YOUR_PROJECT_FOLDER>/<CLIENT_FOLDER>/build
Making changes to this file requires restarting nginx. Restart it.
sudo systemctl restart nginx# ORsudo service nginx restartTip: more commands for nginx
sudo nginx -t # check nginx syntaxsudo systemctl start nginx # start nginxsudo systemctl stop nginx # stop nginxsudo systemctl restart nginx # restart nginxsudo systemctl status nginx # view server statussudo tail -30 /var/log/nginx/error.log # display error log for debuggingAt this point, you should be able to see your app running on server. Navigate to your Public DNS(IPv4) i.e. ec1-4-56-119-211.us-east-2.compute.amazonaws.com. Alternative is to go to IPv4 Public IP i.e. 3.22.154.213
5. Set up your custom domain i.e. route traffic to EC2 Instance
Setting up your custom domain is possible through Route 53 service which is a cheap, paid service (50 cents per month up to 25 hosted zone). Read More about pricing
Go to AWS console and launch Route 53

Start DNS Management
Create Hosted Zone
Type in your domain i.e. yourDomain.com and Create
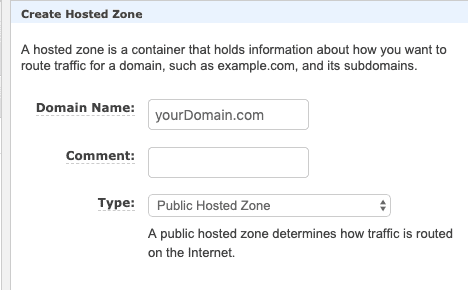
Copy these 4 values, ns-.... then navigate to your domain provider. i.e. namecheap
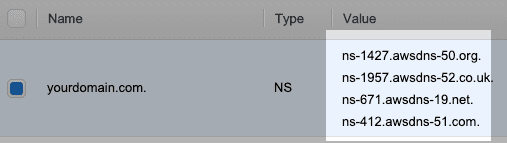
Paste in copied values into Custom DNS name servers on your domain provider's website
Changing name server may take some time depending on the domain provider
6. Set up your SSL certificate (HTTPS)
Certificate validation with domain
AWS Certificate Manager provides a free public SSL/TLS certificates. On AWS console. launch Certificate Manager

Request a certificate
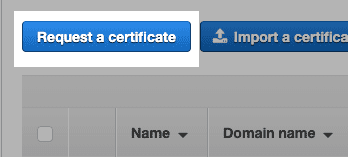
Select Request a public certificate then Request a certificate
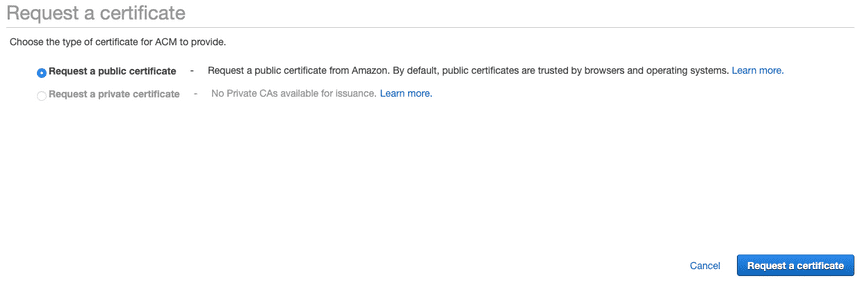
Choose your domain(s). i.e. yourDomain.com and www.yourDomain.com
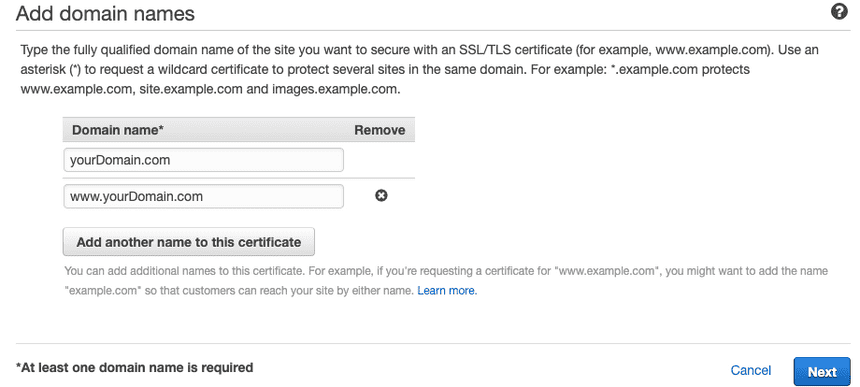
Choose your validation method. DNS validation would be available through Route 53 or other domain name providers such as Namecheap, GoDaddy, etc.
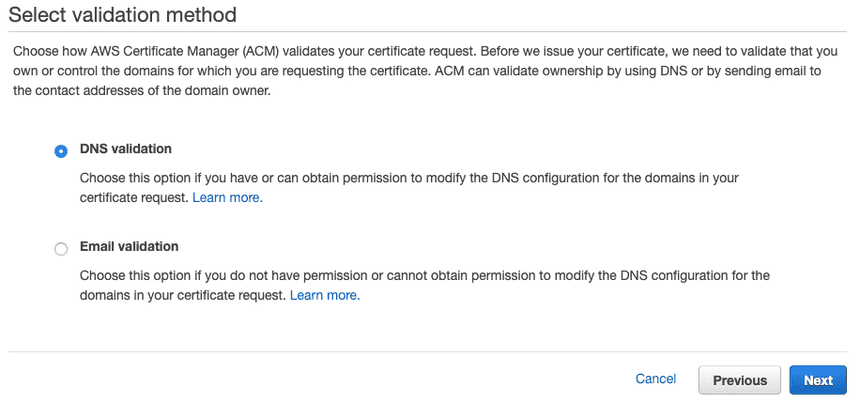
Click Review
Confirm and request
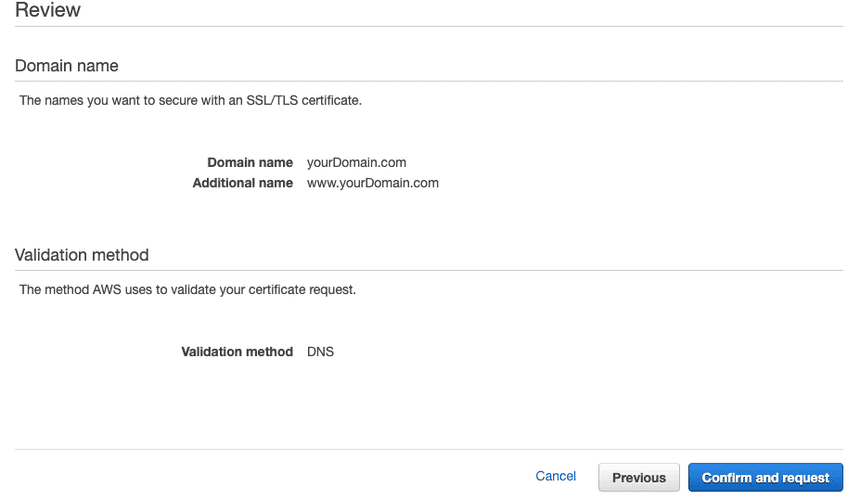
(Route 53 users): if your already using Route 53 with custom domain pointing to your EC2 instance, simply click Create record in Route 53 button(s). Then you'll be able to view created CNAME records in your hosted zone
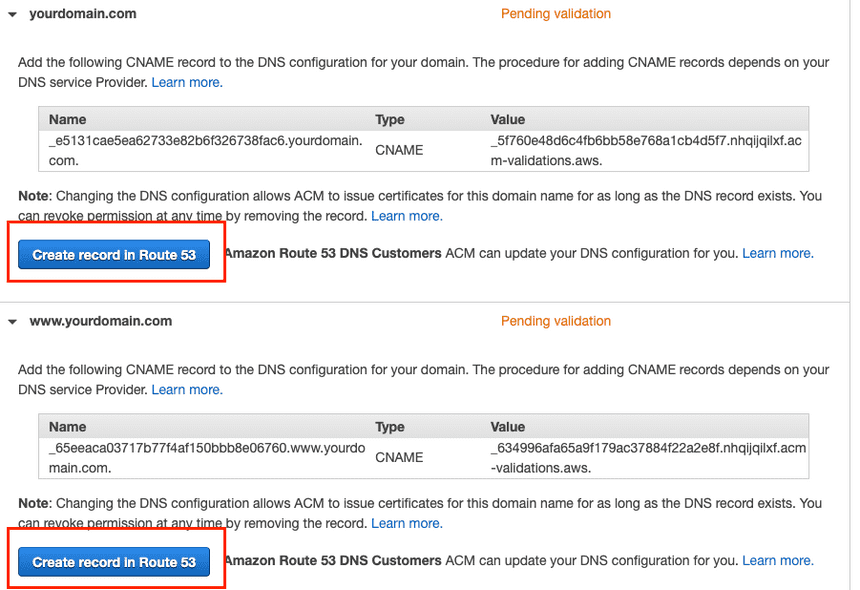
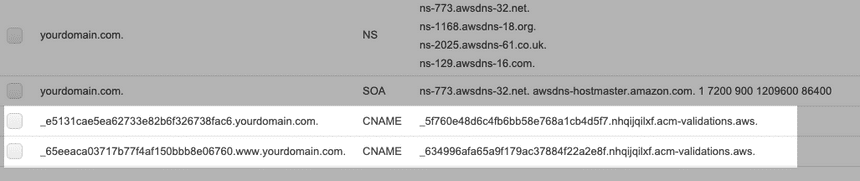
For those who are not using Route 53 and their domain name provider allows to alter DNS record, create these records accordingly
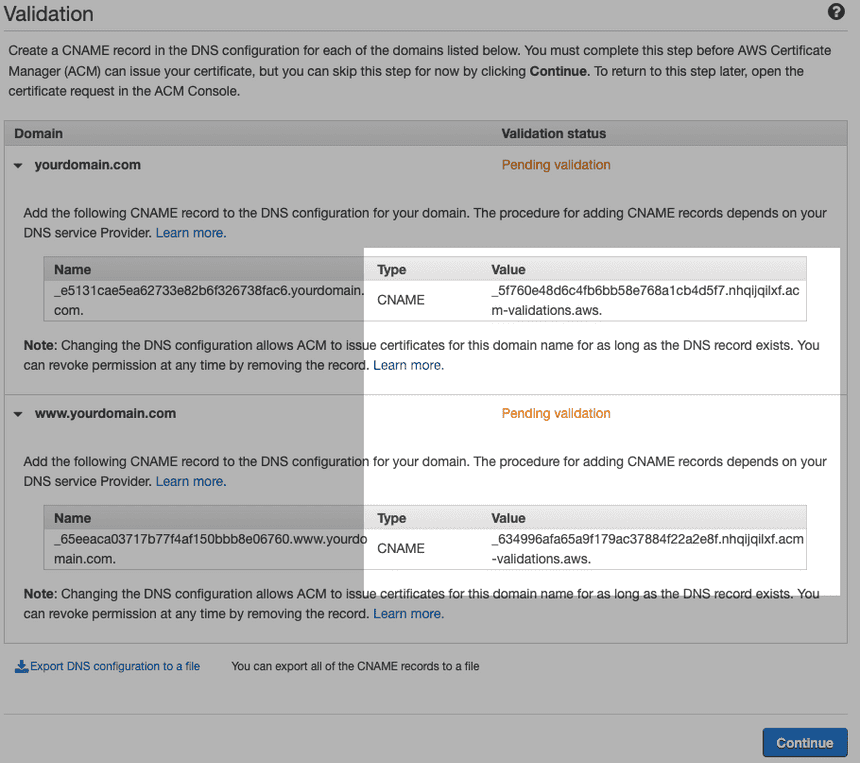
After setting those records, it would typically take about 3-10 minutes to be validated
If DNS validation somehow does not work out, try validating with Email address--Amazon will send verification emails to your registered emails with your domain provider.
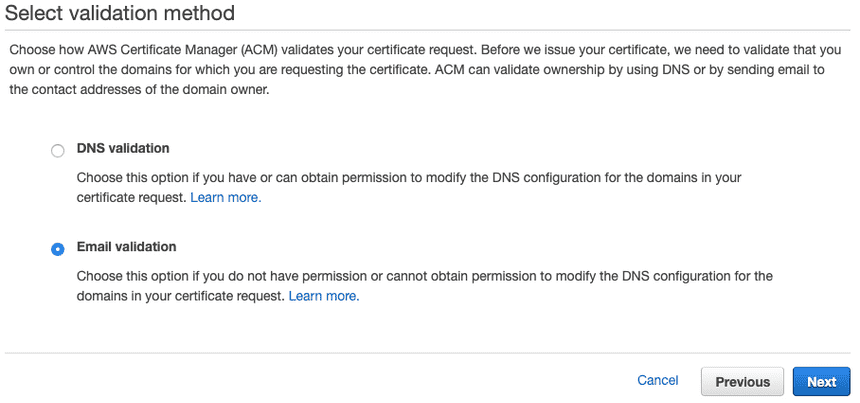
Once you've had your certificate validated with your domain, move onto the next step
Create Load Balancer
Load balancers, in a nutshell, accept users' traffic and reroutes to the right server.
Elastic Load Balancing pricing--this is pretty cheap & your app should have it anyway.
Launch your EC2 instance and click Load balancers from EC2 Dashboard then click Create Load Balancer.
Select Application Load balancer for HTTP/HTTPS
If you'd like, read more about Load balancer Types
Name your balancer, Add listener for HTTPS, and check all availability zones. Then move to Configure Security Settings
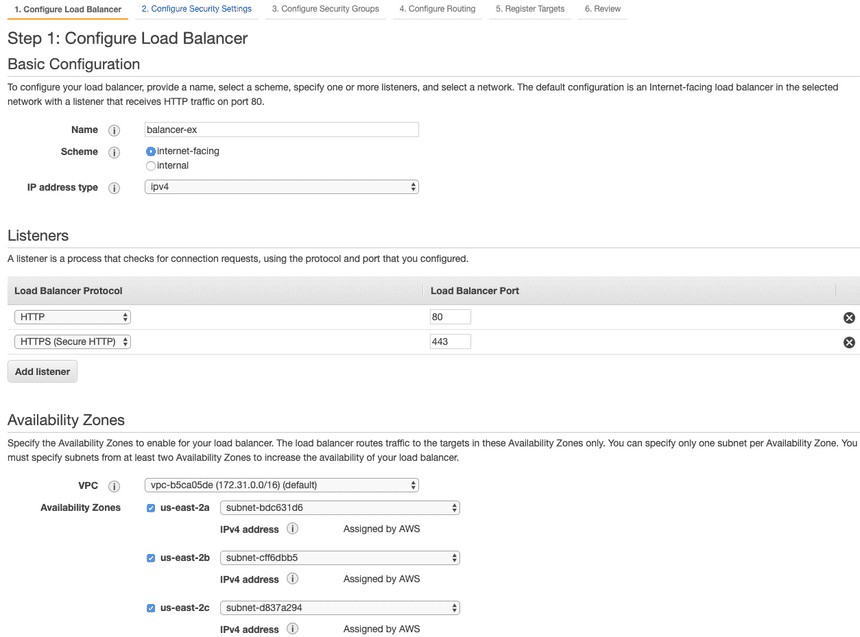
This is where you connect the certificate to your balancer. Select the certificate and move to Configure Security Groups
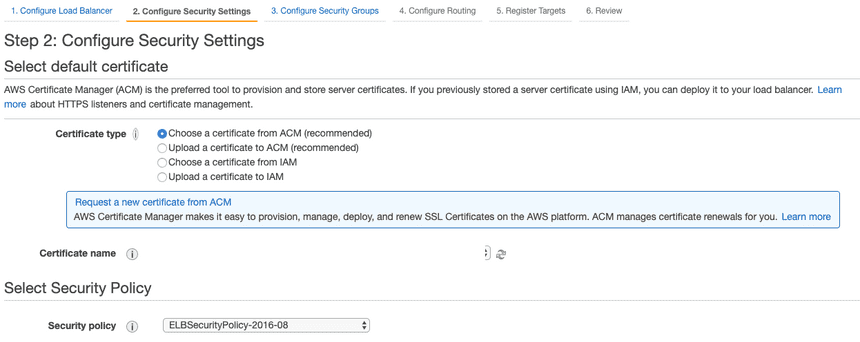
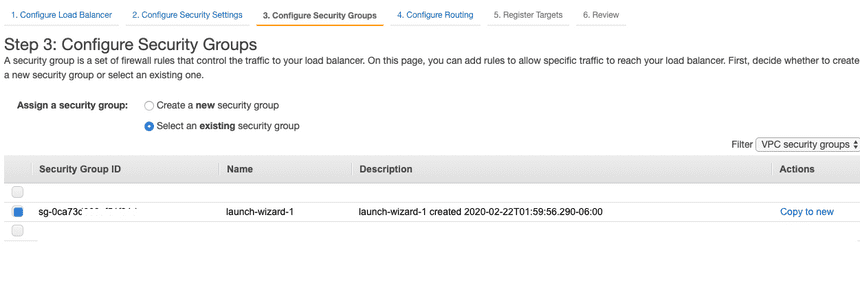
Select the security group that you've previously when creating EC2 instance i.e. launch-wizard-1 then move to next Configure Routing
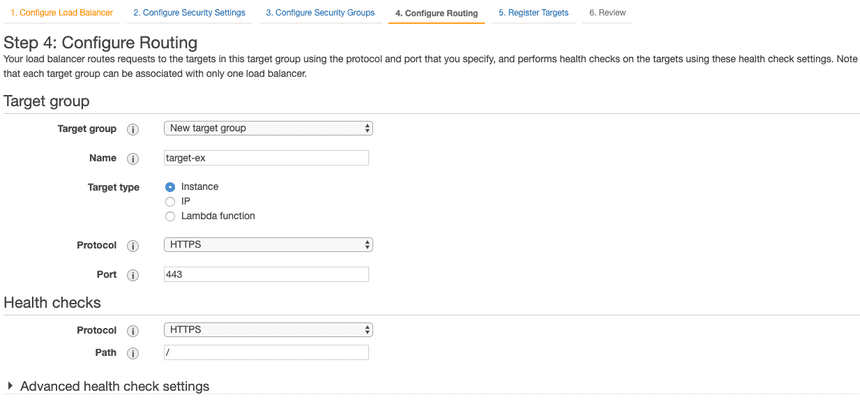
Set new target group with a name and select protocol as HTTPS for target group and for health checks. Move to Register Targets
Check your running instance, Add to registered and check the added instance on upper panel. Then click Next: Review and Create
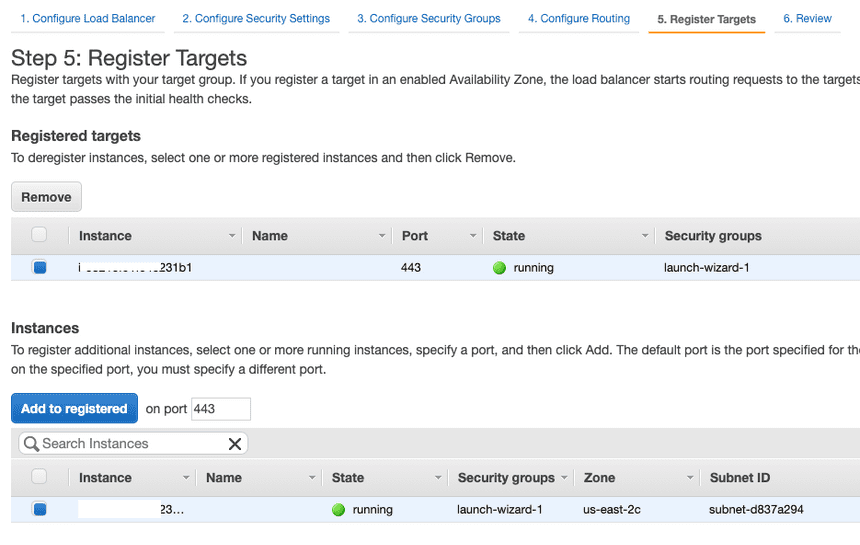
Select the created balancer and click Listeners tab on the lower panel. Select listener for HTTP: 80 then click Edit
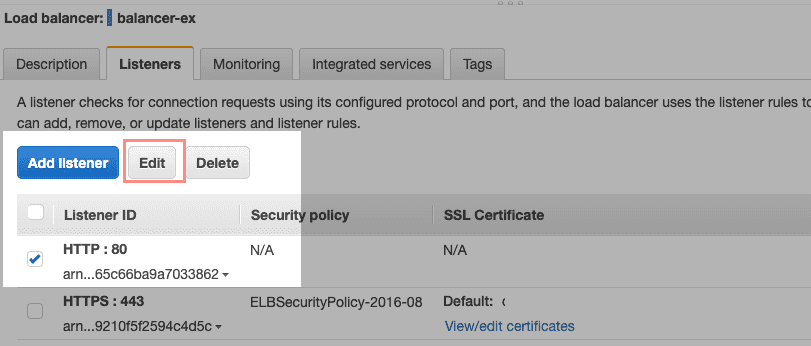
Remove the default action
Then create the following action and click Update
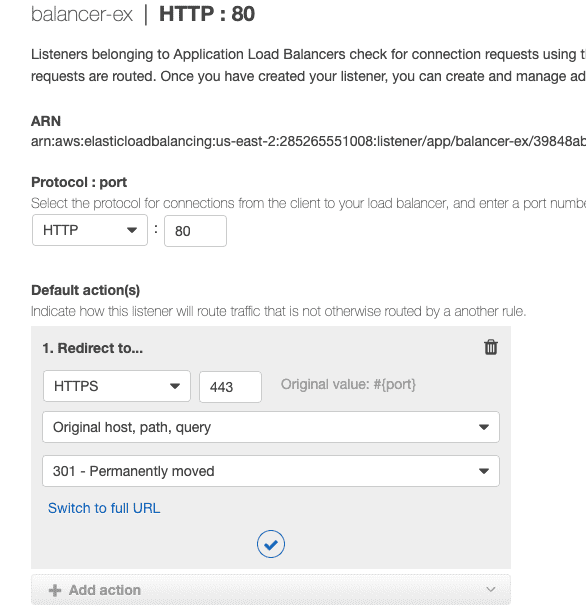
TODO: Missing adding two A(Alias) records to Route53
Modify nginx config & Install certbot
Change content of nginx config
sudo vim /etc/nginx/sites-available/defaultORsudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/defaultChange the server_name to your domain names for rerouting
# Reroute to HTTPSserver { listen 80 default_server; listen [::]:80 default_server; server_name <yourDomain.com> <www.yourDomain.com>; return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;}
server { client_max_body_size 10m; # Increase upload size limit location / { # Connect node api proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080; proxy_http_version 1.1; proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; proxy_set_header Connection 'upgrade'; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade; proxy_redirect off; }}# Install certbotcd ~ && sudo add-apt-repository ppa:certbot/certbot # Then press entersudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install python-certbot-nginx # Then press YRun certbot after installation
sudo certbot --nginx -d yourDomain.com -d www.yourDomain.comIt'll prompt you with..
- Enter your email
- Press "A" to agree
- Y/N whether to share your email
- Press 2 to redirect traffic
Certbot will automatically insert codes inside nginx configuration file:
# Reroute to HTTPSserver { listen 80 default_server; listen [::]:80 default_server; server_name yourDomain.com www.yourDomain.com; return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;}
server { server_name yourDomain.com www.yourDomain.com; # managed by Certbot listen 443 ssl; # managed by Certbot ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/yourDomain.com/fullchain.pem; # managed by Certbot ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/yourDomain.com/privkey.pem; # managed by Certbot include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-nginx.conf; # managed by Certbot ssl_dhparam /etc/letsencrypt/ssl-dhparams.pem; # managed by Certbot
client_max_body_size 10m; # Increase upload size limit
# Check if maintenance is on location / { # Connect node api proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080; proxy_http_version 1.1; proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; proxy_set_header Connection 'upgrade'; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade; proxy_redirect off; }}
server { if ($host = www.yourDomain.com) { return 301 https://$host$request_uri; } # managed by Certbot
if ($host = yourDomain.com) { return 301 https://$host$request_uri; } # managed by Certbot
listen 80 ; server_name yourDomain.com www.yourDomain.com; return 404; # managed by Certbot}This is it! Save default and run sudo systemctl restart nginx to apply change
Create a scheduler to automatically renew your certificate
sudo select-editor # Choose your favorite editorsudo crontab -eInsert this & save
11 23 * * * /usr/bin/certbot renew --quietYour Ubuntu machine will run
/usr/bin/certbot renew --quietevery day at 11:11PM for auto renewal of SSL certificate
Enable maintenance mode for your app
maintenance.html example

<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" /> <title>Ramen Kid | Maintenance</title> <style> body { background: #222; } .main-container-maintenance { position: absolute; top: 40%; left: 50%; font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif; color: #fada26; text-align: center; transform: translate(-50%, -40%); } </style> </head> <body> <div class="main-container-maintenance"> <h1>Offline for maintenance</h1> <p> This website is undergoing maintenance right now (·_·) </p> <p>Please check back later!</p> </div> </body></html>Turning On/Off
When the file exists, your app will only serve maintenance.html. Make sure to put it under directory, /opt/maintenance.html
To turn it on or off
# Turn ONcd /opt && sudo mv maintenance-.html maintenance.html# Turn OFFcd /opt && sudo mv maintenance.html maintenance-.htmlnginx config
Modify nginx config to detect whether there exists /opt/maintenance.html.
sudo vim /etc/nginx/sites-available/default# Reroute to HTTPSserver { listen 80 default_server; listen [::]:80 default_server; server_name yourDomain.com www.yourDomain.com; return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;}
server { server_name yourDomain.com www.yourDomain.com; # managed by Certbot listen 443 ssl; # managed by Certbot ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/yourDomain.com/fullchain.pem; # managed by Certbot ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/yourDomain.com/privkey.pem; # managed by Certbot include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-nginx.conf; # managed by Certbot ssl_dhparam /etc/letsencrypt/ssl-dhparams.pem; # managed by Certbot # Increase upload size limit client_max_body_size 10m;
# Check if maintenance is on location / { if (-f /opt/maintenance.html) { return 503; }
# Connect node api proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080; proxy_http_version 1.1; proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; proxy_set_header Connection 'upgrade'; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade; proxy_redirect off; }
# When /opt/maintenance.html is found error_page 503 @maintenance; location @maintenance { root /opt; rewrite ^(.*)$ /maintenance.html break; }}
server { if ($host = www.yourDomain.com) { return 301 https://$host$request_uri; } # managed by Certbot if ($host = yourDomain.com) { return 301 https://$host$request_uri; } # managed by Certbot listen 80 ; server_name yourDomain.com www.yourDomain.com; return 404; # managed by Certbot}More Notes
- To check remaining space in storage of EC2 instance, run
df -h
- [React + Node.js]: Deploy Your MERN Stack App to Amazon EC2 with SSL Encryption
- [Mac]: Customize your Terminal.app