[React + Node.js]: Create your MERN Stack Application - Part 1: Backend
React
Node.js
03/12/2020
Overview
This post will show you how to create a MERN (MongoDB, Express.js, React, Node.js) Stack Application from the scratch to the end. Part 1 will focus on the server side with REST API. Client side will be covered in the upcoming post, Part 2. This app will involve a basic CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations along with simple layout in React.
The full project is available on this repo.

MongoDB
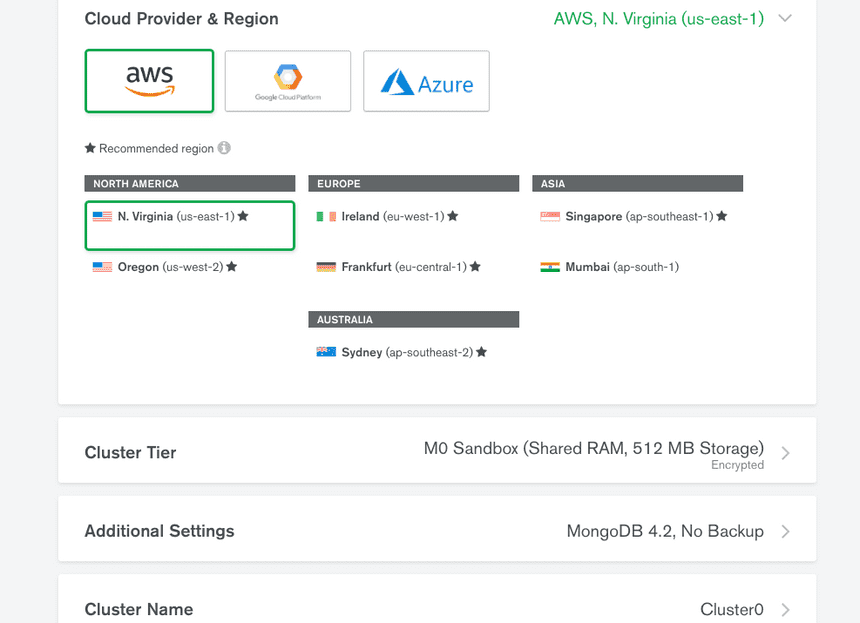
Let's start off with setting the database cluster with MongoDB. If you haven't, go to MongoDB to sign up & sign in. Then, create a free, Starter Clusters with default settings.
Once your cluster is created, press CONNECT
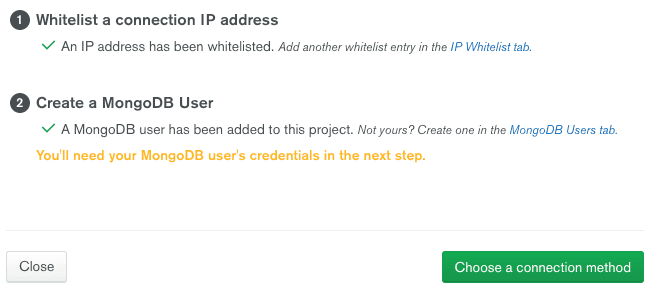
Add your auto-filled IP address to whitelist and create a DB username & password
Choose a connection method as MongoDB Compass. Then follow the instructions to install MongoDB Compass on your system
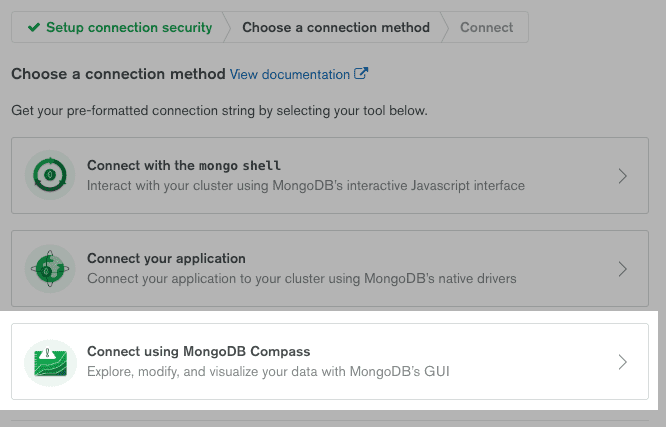
Copy the string that will be used to connect to database in your back-end and in MongoDB Compass
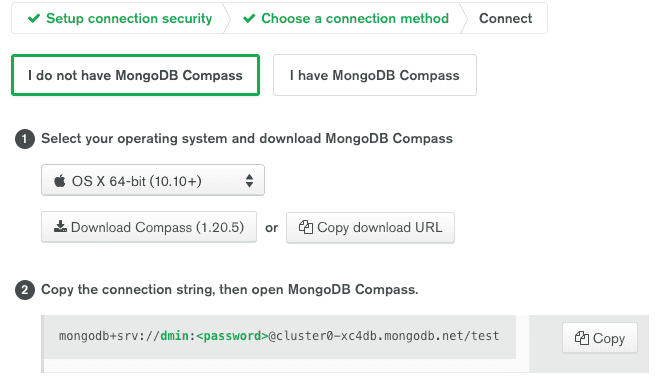
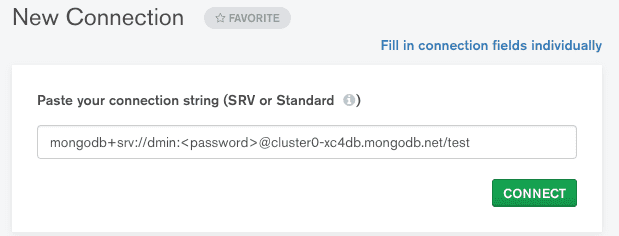
Once installed, connect to MongoDB Compass
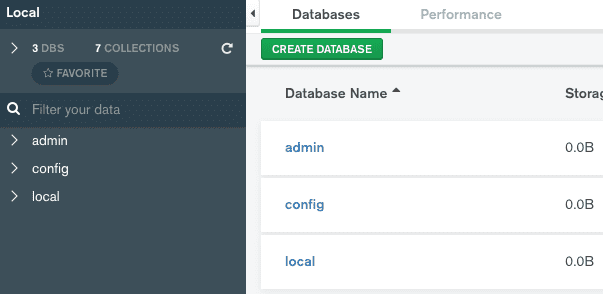
This is where you can visually see & manage data that we haven't created yet. Leave this behind for now and continue to the next step.
Node.js & Express
package.json
mern-demo └── package.json First, create a folder where you would like to contain your MERN stack application. Here, I'll create a folder mern-demo. Then, browse over to the created folder and create package.json with npm init -y command. Make sure that package.json was created and run the following commands to install required node packages.
npm i express mongoose concurrently
concurrentlyallows to run multiple commands concurrently. It'll be used to run back-end and front-end server at the same time
If you have not yet installed nodemon, install it as dev dependency.
npm i -D nodemon
nodemoncontinuously watches the changes in files so that you wouldn't have to restart the server every time you make changes. You can choose to install it globally withsudo npm i -g nodemon
With those packages installed, modify "scripts" in package.json to start developing.
"scripts": {- "test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"+ "start": "node app.js",+ "server": "nodemon app.js",},config.js & app.js
mern-demo ├── app.js ├── config.js └── package.jsonCreate config.js that will contain your MongoDB URI that you've copied
config.js
module.exports = { MONGODB_URI: `mongodb+srv://<DB_USERNAME>:<PASSWORD>@cluster0-xc4db.mongodb.net/test`,}Then create app.js. This is the main server that will listen to the request from the client side
app.js
const express = require("express")const mongoose = require("mongoose")const { MONGODB_URI } = require("./config")
const app = express()app.use(express.json())
// Set CORS headerapp.use((req, res, next) => { res.setHeader("Access-control-Allow-Origin", "*") res.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "GET, POST, DELETE") // Allow client to set headers with Content-Type res.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "Content-Type") next()})
// Error Handlerapp.use((error, req, res, next) => { const status = error.statusCode || 500 const message = error.message const data = error.data // Passing original error data res.status(status).json({ message: message, data: data })})
// DB connectionmongoose .connect(MONGODB_URI, { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true, useFindAndModify: false, }) .then(result => { const port = process.env.PORT || 8080 app.listen(port, () => { console.log(`Listening on port ${port}...`) }) }) .catch(err => { // Handle error })At this point, when you run
npm server, the server will start listening to port 8080
User Schema
mern-demo ├── models | └── user.js ├── app.js ├── config.js └── package.jsonconst mongoose = require("mongoose")const Schema = mongoose.Schema
const userSchema = new Schema( { name: { type: String, required: true, }, age: { type: String, required: true, }, occupation: { type: String, required: true, default: "unemployed", }, }, { timestamps: true })
module.exports = mongoose.model("User", userSchema)Each user will have 3 properties: name, age, occupation
Router & Controller
mern-demo ├── controllers | └── user.js ├── routes | └── user.js ├── models | └── user.js ├── app.js ├── config.js └── package.jsonroutes/user.js
const express = require("express")const userController = require("../controllers/user")const router = express.Router()
// GET /userrouter.get("/user", userController.getUsers)// POST /userrouter.post("/user", userController.postUser)// DELETE /user/:userIdrouter.delete("/user/:userId", userController.deleteUser)module.exports = routerRouter here defines the 3 CR
UD operations
controllers/user.js
const User = require("../models/user")
exports.getUsers = async (req, res, next) => { try { const users = await User.find().sort({ createdAt: -1 }) res.status(200).json({ message: "Fetched users", users: users, }) } catch (err) { if (!err.statusCode) { err.statusCode = 500 } next(err) }}
exports.postUser = async (req, res, next) => { try { let occupation = req.body.occupation if (!occupation) occupation = "unemployed" const user = new User({ name: req.body.name, age: req.body.age, occupation: occupation, }) await user.save() // Save in db
res.status(201).json({ message: "User created", user: user, }) } catch (err) { if (!err.statusCode) { err.statusCode = 500 } next(err) }}
exports.deleteUser = async (req, res, next) => { const userId = req.params.userId try { const user = await User.findById(userId) if (!user) { const error = new Error("Couldn't find the user") error.statusCode = 404 throw error } await User.findByIdAndRemove(userId) res.status(200).json({ message: "User removed" }) } catch (err) { if (!err.statusCode) { err.statusCode = 500 } next(err) }}Register Created Route
app.js
const express = require("express")const mongoose = require("mongoose")const { MONGODB_URI } = require("./config")const userRoutes = require("./routes/user")
const app = express()app.use(express.json())
// Set CORS headerapp.use((req, res, next) => { res.setHeader("Access-control-Allow-Origin", "*") res.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "GET, POST, DELETE") // Allow client to set headers with Content-Type res.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "Content-Type") next()})
// Register Routeapp.use(userRoutes)
// Error Handlerapp.use((error, req, res, next) => { const status = error.statusCode || 500 const message = error.message const data = error.data // Passing original error data res.status(status).json({ message: message, data: data })})
// DB connectionmongoose .connect(MONGODB_URI, { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true, useFindAndModify: false, }) .then(result => { const port = process.env.PORT || 8080 app.listen(port, () => { console.log(`Listening on port ${port}...`) }) }) .catch(err => { // Handle error })What's next? 🤔
- [React + Node.js]: Create your MERN Stack Application - Part 2: Frontend
- [Deploy]: Deploy your App on Netlify
- [React + Node.js]: Create your MERN Stack Application - Part 2: Frontend